Bindings in Angular-Types and Usages
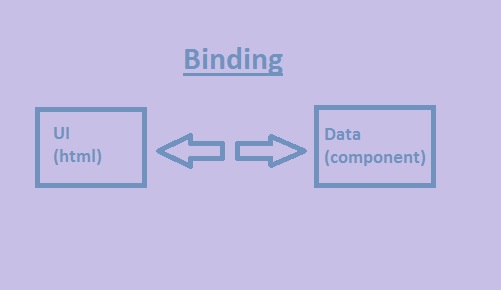
What is Binding?
It defines the connection between the UI of the application( HTML) and the data coming from some business logic through components.
Here we will discuss different types of bindings in Angular. basically, there are 3 types of bindings, but there are few variations of it, will discuss all of them.
- Property Binding
- Event Binding
- Two-way Binding
Property Binding
It works one side that is the direction of binding is from component to DOM. Any change in the properties of the component is reflected in the DOM.
In property binding, we define the dom element in the square bracket [] to which the binding should reflect.
<img [src]="imageUrl">
Here src is the dom element and imageUrl is the property that is bind from the component.
Code in the Component file is as below:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
...
imageUrl:any;
constructor() { }
ngOnInit() {
this.imageUrl="https://www.google.com/images/branding/googlelogo/1x/googlelogo_color_272x92dp.png";
}
...
Once we render the page we can see the image as below:
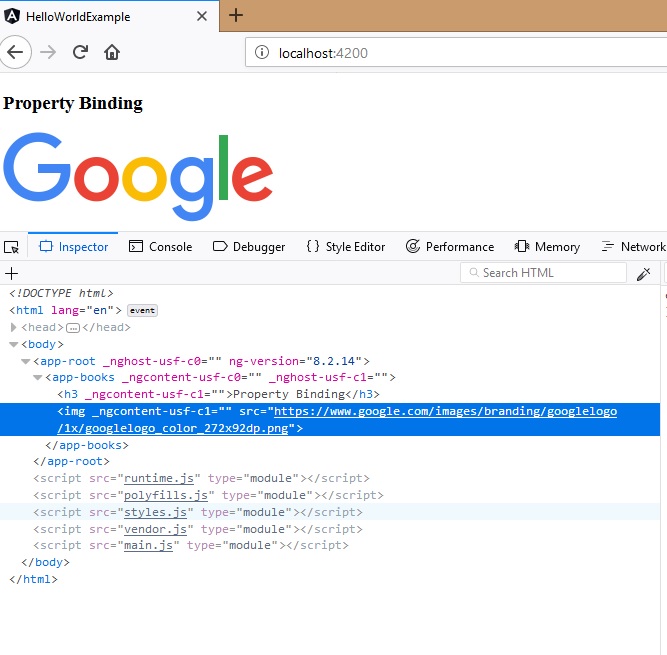
As you can see the URL value is bind to the src attribute in the img element of html.
Some of the variations of the property binding are:
- String Interpolation
- Attribute Binding
- Class Binding
- Style Binding
String Interpolation
In string interpolation, the property or field in the component is bind in a special syntax called string interpolation syntax with two curly brackets {{}} .
An example of the same is provided in this article.
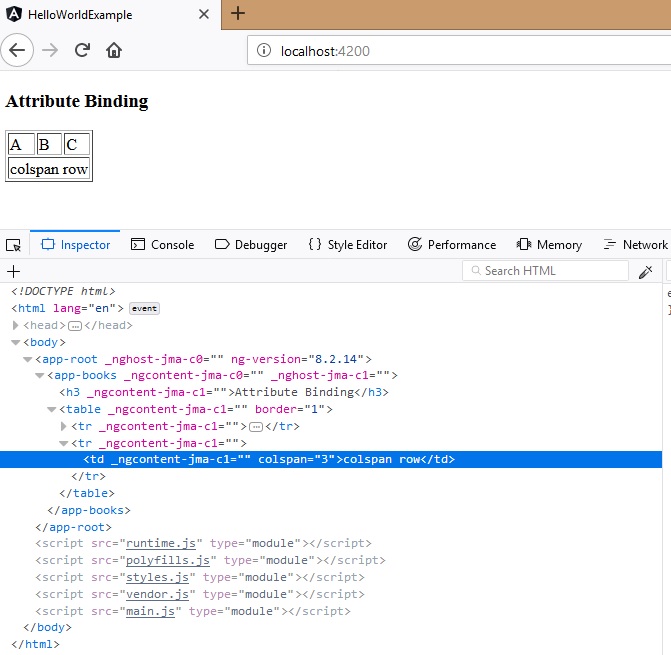
Attribute Binding
Similar to property binding only the main difference here is that we use attributes to reference the dom element. Why we use this approach is because there may come situations where we cannot identify direct DOM elements to bind for some html elements. eg. colspan.In order to bind dynamic values to those fields, we use attribute binding.
Sample code in html and components are as follows:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
<table border="1">
<tr>
<td> A</td>
<td> B</td>
<td> C</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td [attr.colspan]="colspan"> colspan row</td>
</tr>
</table>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
...
export class BooksComponent implements OnInit {
colspan:number
constructor() { }
ngOnInit() {
this.colspan=3;
}
}
...
When the page renders you can see below the output and value of the colspan bound properly.
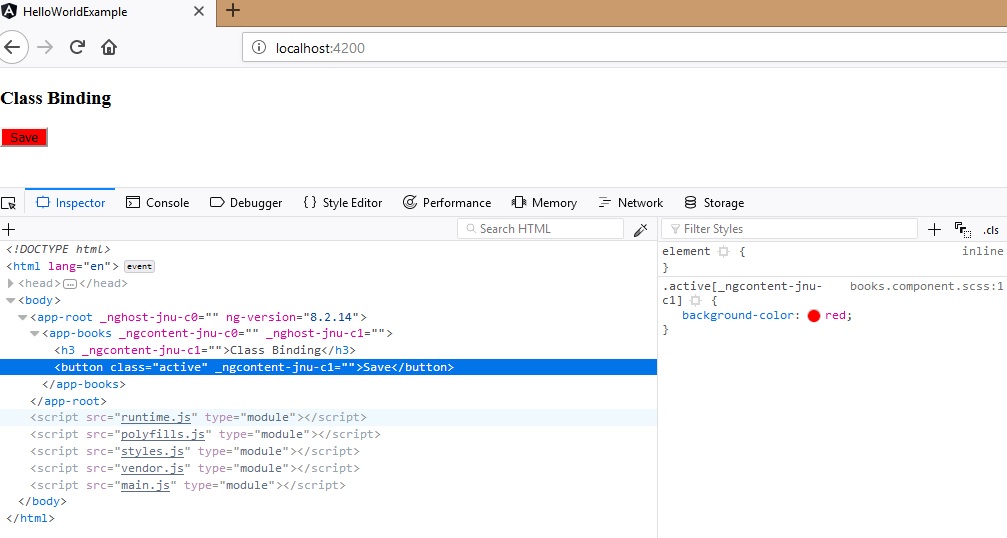
Class Binding
In class binding syntax is the same as square bracket and we mention the class to be added to the html element as:
<button \[class.active\]="isActive">Save</button>
Here active is the class name to be added or remove and isActive the property from the component based on which class is added dynamically.
The code in the component is as below:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
export class BooksComponent implements OnInit {
isActive:boolean
constructor() { }
ngOnInit() {
this.isActive=true;
}
}
We have added a style class in the scss file as below:
1
2
3
.active{
background-color: red;
}
Once we render the page we can see below style in button, also we can see the class added to the html element.
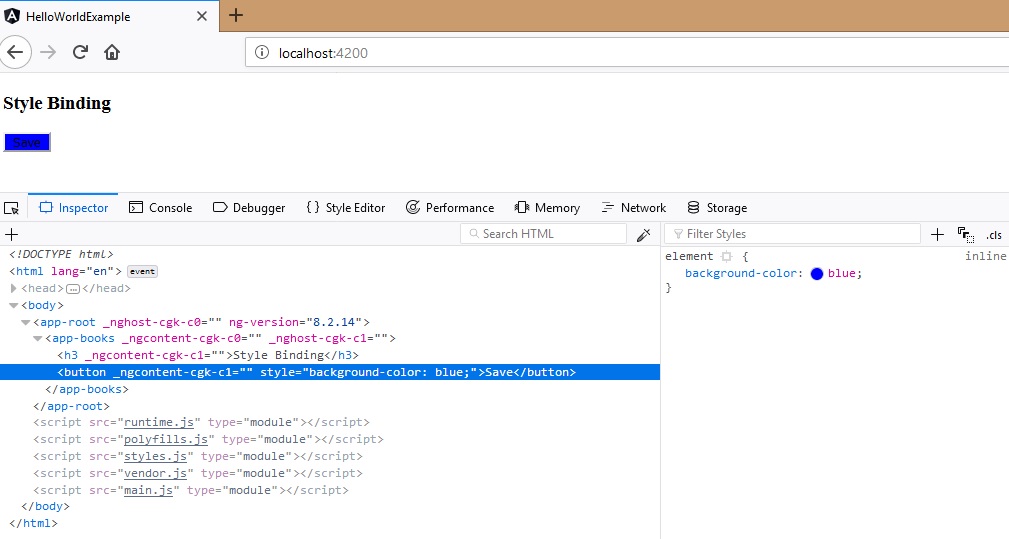
Style Binding
Functionality is the same as class binding, the only difference is that instead of class we use style, and instead of class name we use CSS styles defined. code in html is as below:
<button \[style.backgroundColor\]="isActive? 'blue':'grey'">Save</button>
For the same code in the component the page will render as below with inline style added to html element.
Event Binding
In event binding, we bind the event to some function inside the component. So the method of communication is from UI to the component. the syntax of it is that the event is enclosed in round brackets as shown below:
<button (click)="onSave()">Save</button>
In order to access the event object we can pass it as shown below:
<button (click)="onSave($event)">Save</button>
$event is the standard event object in angular. To stop the propagation of the event we can mention the below code in the component function, where $event signifies the event object passed to the function.
$event.stopPropagation();
The component code is as below:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
export class BooksComponent implements OnInit {
constructor() { }
ngOnInit() {
}
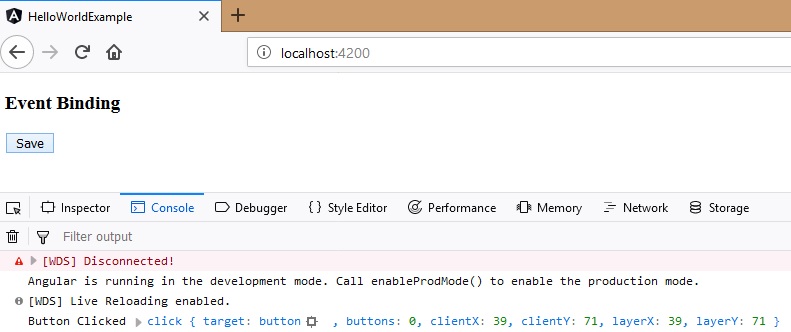
onSave(event) {
console.log('Button Clicked',event);
event.stopPropagation();
}
}
Finally, when we click the button we get the below message in the console.
Two-way Binding
The final and most important binding method is two-way binding. Here changes in the property can be passed in both ways from UI to component and vice versa. The syntax for two-way binding is [(ngModel)]=”propertyname”. In order to use it, we need to import FormsModule to our app.module.ts file
1
2
3
4
5
6
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
...
imports: [
...
FormsModule
]
Code in the html is as below: Here we use keyUp event binding with filtering option which is called Event filtering
<input \[(ngModel)\]="email" (keyUp.enter)="onKeyUp()"/>
Code in component is as follows:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
export class BooksComponent implements OnInit {
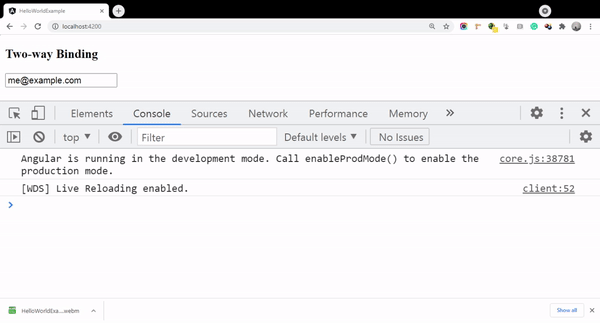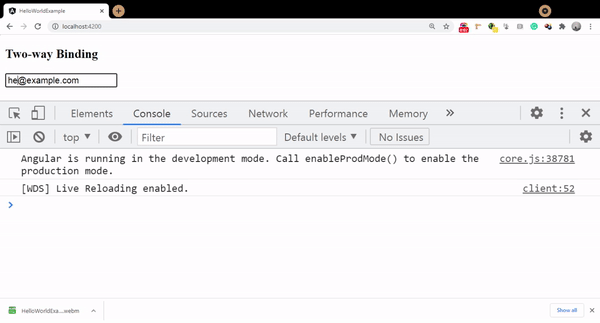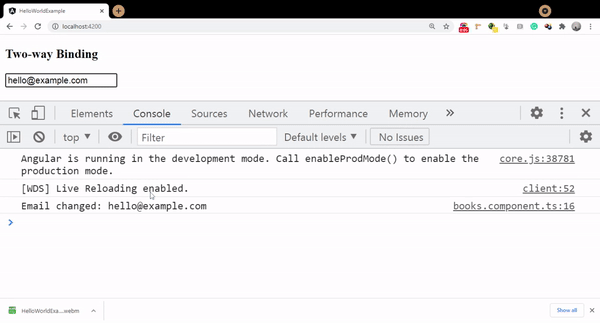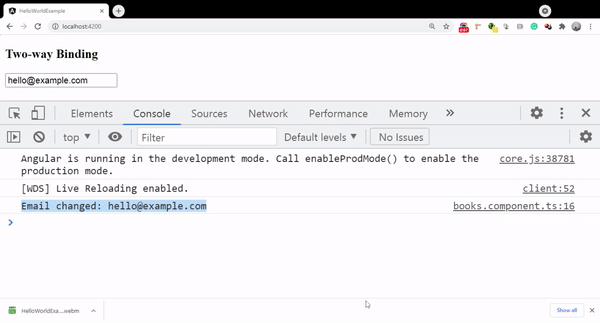
email="me@example.com"
constructor() { }
ngOnInit() { }
onKeyUp()
{
console.log('Email changed:',this.email);
}
}
Initially, the value of the email field is bind as me@example.com and once we update it the same property has updated value reflected in the component as well.
The functionality of the two-way binding is clear from below demo video:
Hope you get an idea about different types of bindings and how to use it. Do let us you if you have any clarifications or feedbacks.